
Top Selling Products
-
Helax Tabler 50's pack
৳144.00 -
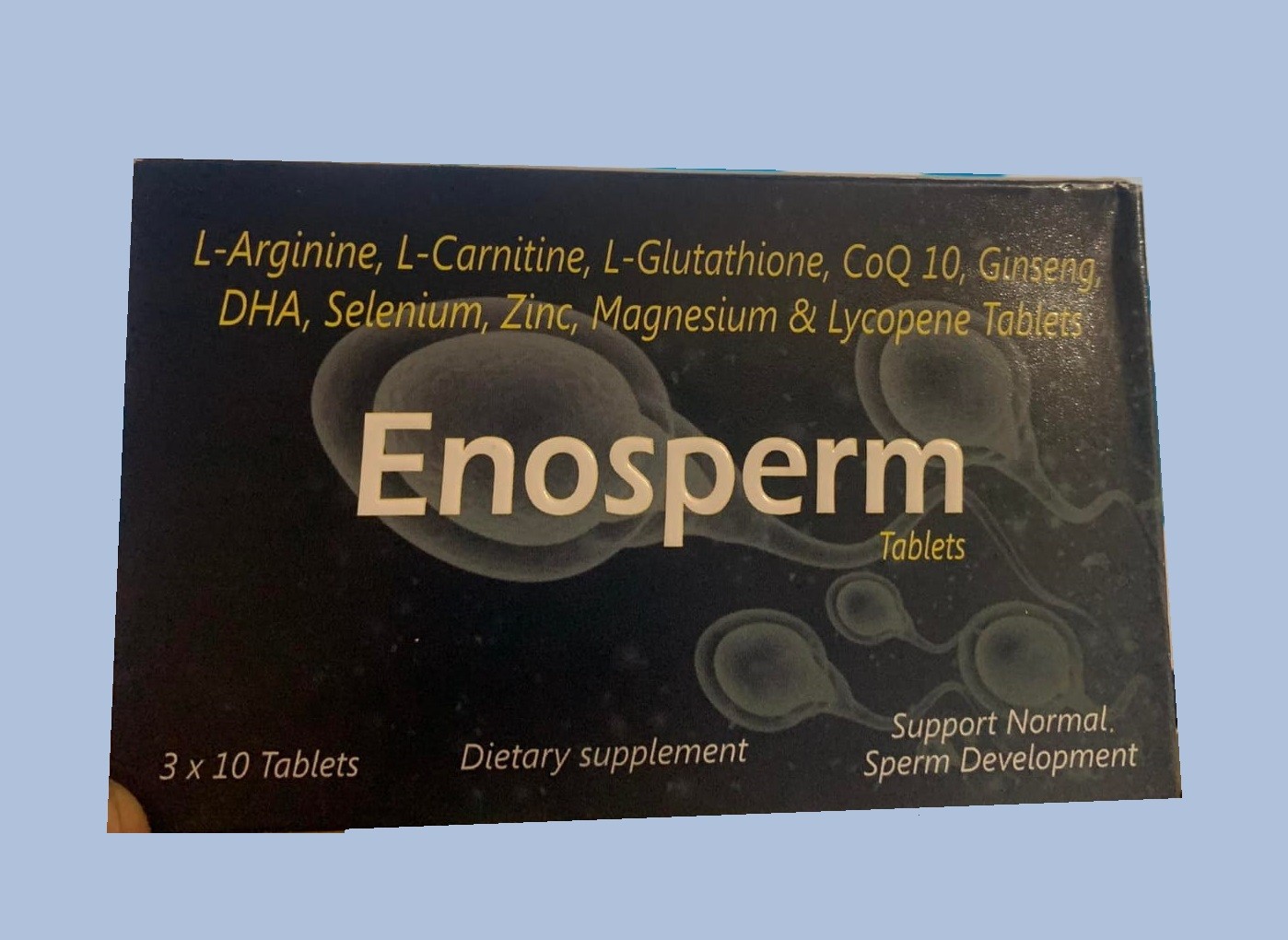
Enosperm Tablet 30 pcs
৳1,620.00 -
Glow Briss Face Wash 100 ml
৳1,081.00 -
Inosia-F Tablet 30 pcs
৳1,757.80 -
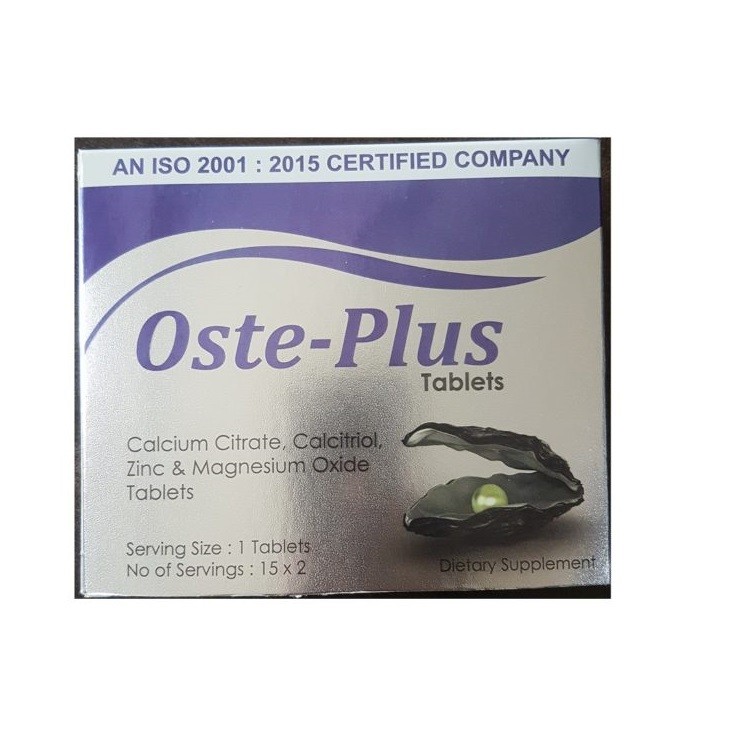
OSTE-Plus Tablet 30's pack
৳653.30
Indications
Prochlorperazine Maleate is indicated
·
Relieving nausea, vomiting, and attacks of
dizziness or spinning sensations (vertigo) associated with Meniere's disease
and other inner ear disorders.
·
For the treatment of psychotic illness such as
schizophrenia (hallucinations and hostility).
·
Acute mania.
·
For the short-term treatment of generalized
non-psychotic anxiety.
· To control severe nausea and vomiting caused by radiation therapy, cancer chemotherapy, surgery, and other conditions.
Dosage & Administration
Children (not recommended in children <10 kg or <2 years):
10-14 kg: 2.5 mg every 12-24 hours as needed; maximum: 7.5 mg/day
15-18 kg: 2.5 mg every 8-12 hours as needed; maximum: 10 mg/day
19-39 kg: 2.5 mg every 8 hours or 5 mg every 12 hours as needed;
maximum: 15 mg/day.
Adults: 5-10 mg 3-4 times/ day; usual maximum: 40 mg/day
Antipsychotic Children (not recommended in children <10 kg or <2
years):
2-12 years: 2.5 mg 2-3 times/day Increase dosage as needed to a maximum
daily dose of 20 mg for 2-5 years and 25 mg for 6-12 years Adults: 5-10 mg 3-4
times/day; doses up to 150 mg/day may be required in some patients for
treatment of severe disturbances
Nonpsychotic anxiety Adults: Usual dose: 15-20 mg/day in divided doses;
do not give doses >20 mg/day or for longer than 12 weeks Elderly: Initial:
2.5-5 mg 1-2 times/day; increase dose at 4 to 7 day intervals by 2.5-5 mg/day;
increase dosing intervals (twice daily, thrice daily, etc) as necessary to
control response or side effects; maximum daily dose should probably not exceed
75 mg in elderly; gradual increases (titration) may prevent some side effects
or decrease their severity.
Prochlorperazine may be administered without regard to the meal.
Interaction
Alcohol, barbiturate & other sedatives may increase the CNS depressant action. Some drugs like Antacids, antiparkinson's drug, lithium may interfere the absorption of Prochlorperazine. This drug may interfere with the plasma concentration of Propanolol and Phenobarbital.
Side Effects
Drowsiness; jaw, neck, and back muscle spasms; fine worm-like tongue movements; rhythmic face, mouth, or jaw movements; slow or difficult speech; difficulty swallowing; restlessness and pacing; tremors; shuffling walk; skin rash; yellowing of the skin or eyes.
There have been no reviews for this product yet.